What if we can control applications through our eyes then select features by a gaze? what if we can interact with Augmented holograms?
Yup! it is not Science Fiction anymore -- There comes Mixed Reality(XR)
Analysts predict that head-mounted mixed reality glasses will over time replace most of the physical screens that we use today including computer screens, smartphones, tablets, etc.
What is Mixed Reality?
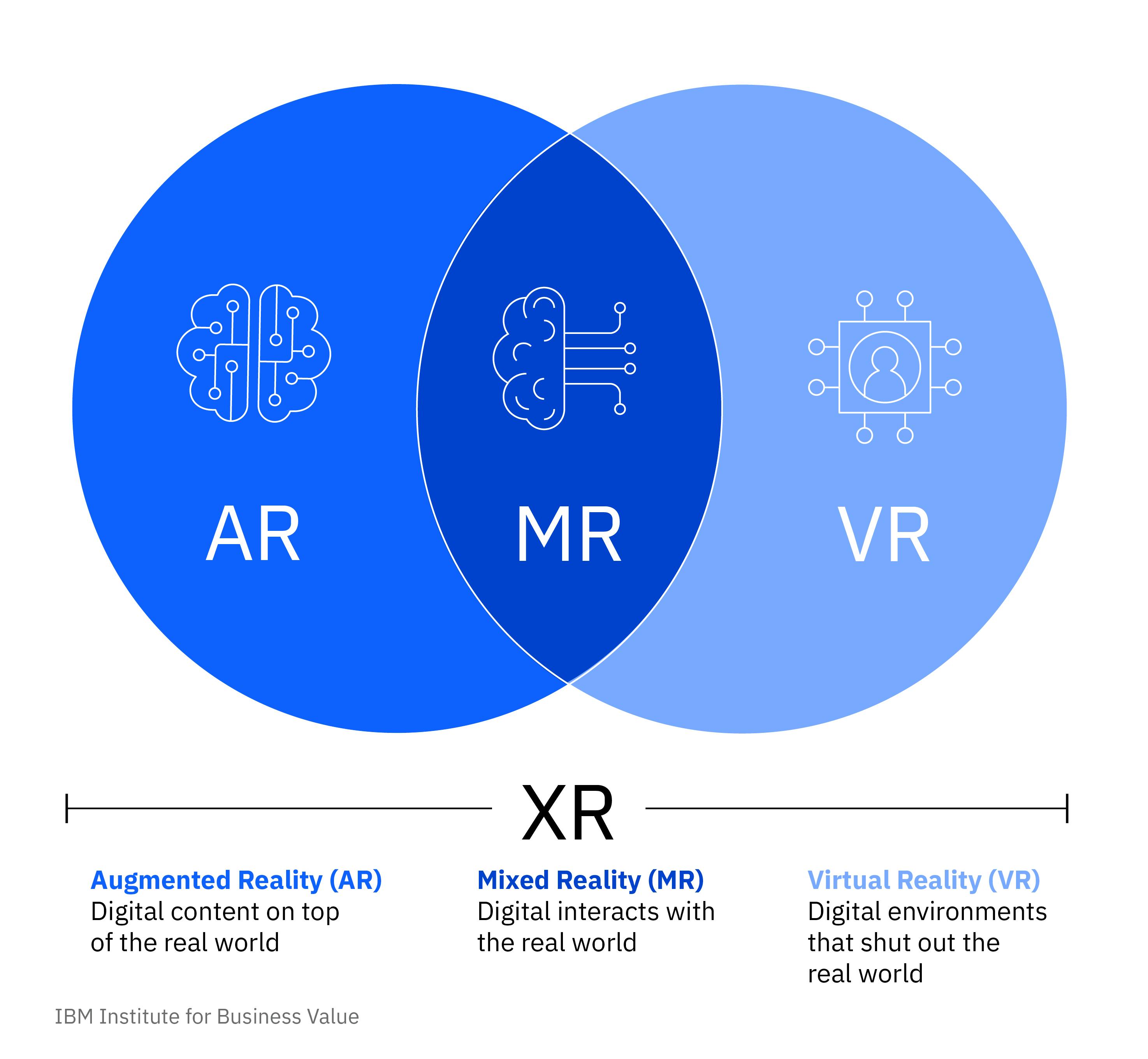
Before that let us see what is Virtual and Augmented reality as Mixed Reality(XR) is a blend of both VR & AR.
Augmented Reality:
To put it in simple words, 'AR' is a technology that creates a composite viewing experience by superimposing a computer-generated image over a user's view of the real world.
Augmented reality experiences aren't limited to visual additions to our world. You can create augmented experiences that are only audio additions to your physical world, or both audio and visual.

Augmented reality experiences are not limited to headsets like HoloLens. Today, millions of mobile devices have depth-sensing capabilities to augment the real world with digital information.
Virtual Reality:
VR is a technology or experience that absolutely immerses a user into a virtual world through the use of a headset, effectively severing their connection to the sights and sounds of the real world.

Virtual reality applications are great for gaming, training, and for simulations where users would benefit from total immersion to replicate a real-life situation. Examples include training for firefighters, training for emergency-room healthcare providers, and flight simulations.
Mixed Reality:
Mixed reality is a spectrum of immersive experiences, connecting and blending physical and digital worlds together in augmented reality and virtual reality applications.
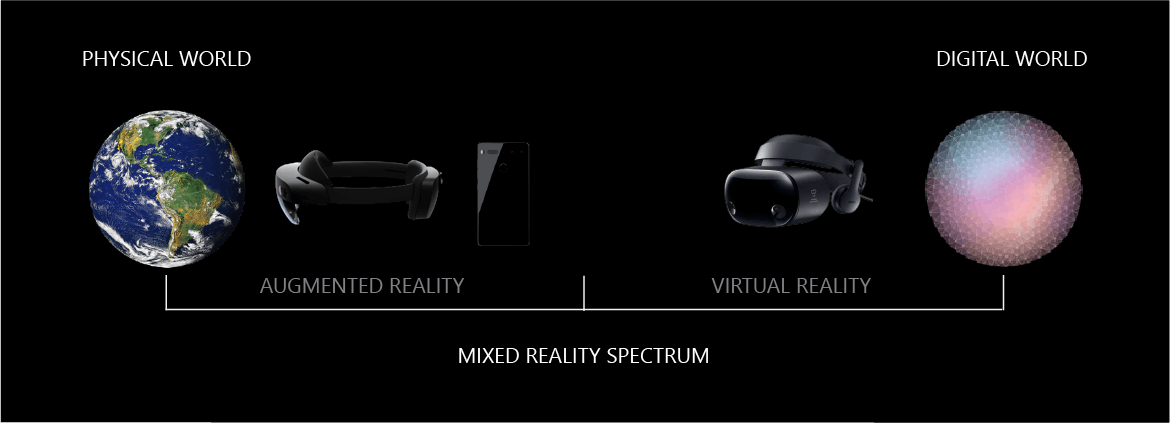
Because mixed reality covers such a broad range of possible user experiences, it comes with a set of interaction types that are entirely unique.
These interaction types include but are not limited to:
- Environmental input, like capturing a user's position in the world by mapping surfaces and boundaries in the area.
- Spatialized sound, which is a 3D sound that has position and depth in a virtual space, just like in the real world.
- Locations, positions, and persistence of objects in real and virtual spaces.
These features are part of a relationship between human and computer input known as human-computer interaction (HCI).
Human input covers the more familiar ways of interacting with technology, such as using a keyboard, mouse, touchpad, or your own voice. As sensors and processing power have increased in computers, so has this new area of computer input from the environment.
The interaction between computers and the environment is called perception.
Mixed Reality devices:
Now that we've covered the conceptual differences between virtual reality experiences and augmented reality experiences, and where they fit into mixed reality, we can look at the hardware devices that you can develop with.
HoloLens
For applications and games on the augmented reality side of the spectrum, you would target Microsoft HoloLens.

HoloLens has a see-through display so users can see the physical environment around them while wearing the headset, with a full six-degrees-of-freedom movement for both rotation and translation.
For virtual reality experiences, you can develop for a wide range of Windows mixed reality immersive headsets like the Samsung HMD Odyssey+ or HP Reverb G2. These devices have opaque displays that block out the physical environment and have full six-degrees-of-freedom movement to immerse users in a virtual world.
If you're creating an application that relies on the physical world around the user, HoloLens is the best bet. If you're going to throw your users into the deep end of the spectrum, then a Windows mixed reality immersive headset is the way to go.
Holograms:
Holograms and holographic experiences aren't science fiction anymore. In fact, they make up the foundation of all augmented reality applications.

Holograms are digital objects that appear in the world around the user who's wearing a HoloLens headset. They're made of light and sound. You can program holograms to interact with a user's gaze, gestures, or voice input. An example is rotating a digital building plan with the touch of a finger or wave of a hand.
It's important to note that holograms are only part of the augmented reality portion of the mixed reality spectrum. They shouldn't be confused with virtual objects in immersive experiences.
One of the most wonderful aspects of holograms and augmented reality is that they can appear to interact with the physical world.
For example, you can place a holographic ball above a table in the real world and have it bounce when a user makes a gesture or says the word "bounce." Adding sound effects or occlusion behind real-world objects can give your holograms added physicality and realness.
Mixed reality development tools:
When it comes to working with holograms in your applications, it's easiest to use some of Microsoft's premade development tools, like the Mixed Reality Toolkit (MRTK) for Unity and Unreal Engine.
 MRTK is an open-source, cross-platform development kit that provides an input system, foundational components, and common building blocks for spatial interactions.
MRTK is an open-source, cross-platform development kit that provides an input system, foundational components, and common building blocks for spatial interactions.
Microsoft's Mixed Reality Toolkit
Use cases of Mixed Reality:
To be able to process the data and make informed decisions, we need to have access to the data at the right time and right place. In the future, we'll be looking to mixed reality to bring that data into our context, the real world.
Common use cases
- Design and prototyping: Enables real-time collaborative iteration of 3D physical and virtual models across cross-functional teams and stakeholders.
- Training and development: Provides instructors with better tools to facilitate teaching or coaching sessions. It offers trainees an enhanced and engaging learning experience through 3D visualizations and interactivity.
- Geospatial planning: Enables the assessment and planning of indoor and outdoor environments. Examples are future construction sites, new store locations, and interior designs. It also removes the need for manual execution.
- Sales assistance: Improves the effectiveness of individuals in sales-oriented roles by providing tools that increase customer engagement and strengthen buyer confidence. These tools include 3D catalogs and virtual product experiences.
- Field service: Improves the first-visit resolution and customer satisfaction of customer support issues. It's typically used for complex products that would otherwise require a field visit. It can also serve as a platform for targeted up-sell opportunities.
- Productivity and collaboration: Transforms the space around you into a shared augmented workplace. Remote users can collaborate, search, brainstorm, and share content as if they're in the same room.

Augmented reality is already available on smartphones and tablets. Mixed reality is in its infancy with Microsoft as the market leader and Magic Leap pushing to be the next big contender in the market.
Outro:
Hope it helps you to understand the difference between AR, VR, and XR and gives you a simple understanding of Mixed reality, its future and how can it be applied in our real world.
If you are interested in creating your own Mixed Reality Environments, I would encourage you to explore Microsoft's Mixed Reality ToolKit.
for more info:
Thankyou😊
Happy Learning
-JHA